OXLUMO® (lumasiran)
Person with PH1
*Alnylam is proud to feature real patients in our advertising. Patients may or may not be on an Alnylam therapy.
OXLUMO® (lumasiran) is the first FDA-approved treatment for primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1) to lower urinary and plasma oxalate levels in infants, children and adults.1-3
A targeted RNAi treatment backed by the largest clinical trial program in PH11,4
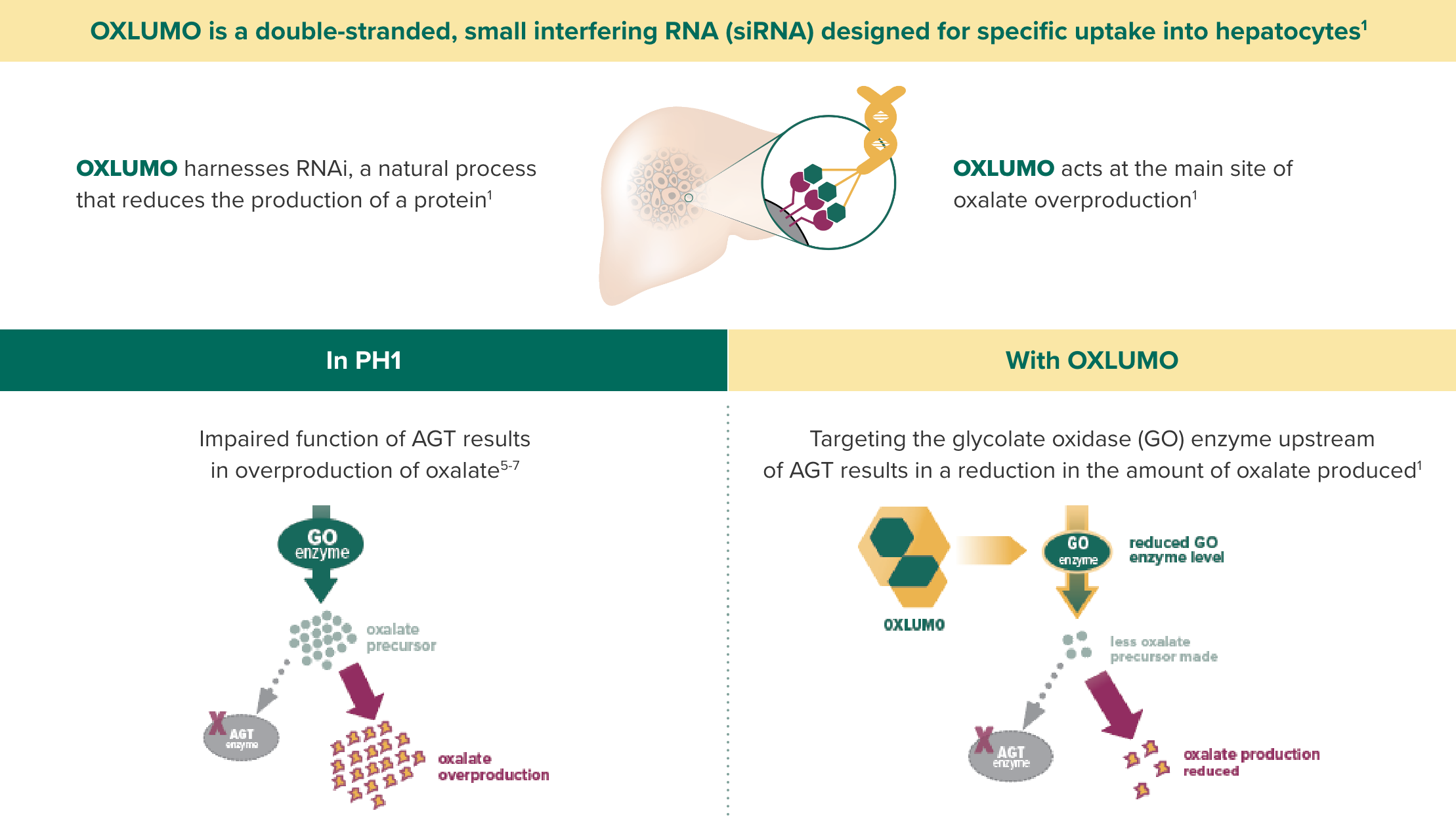
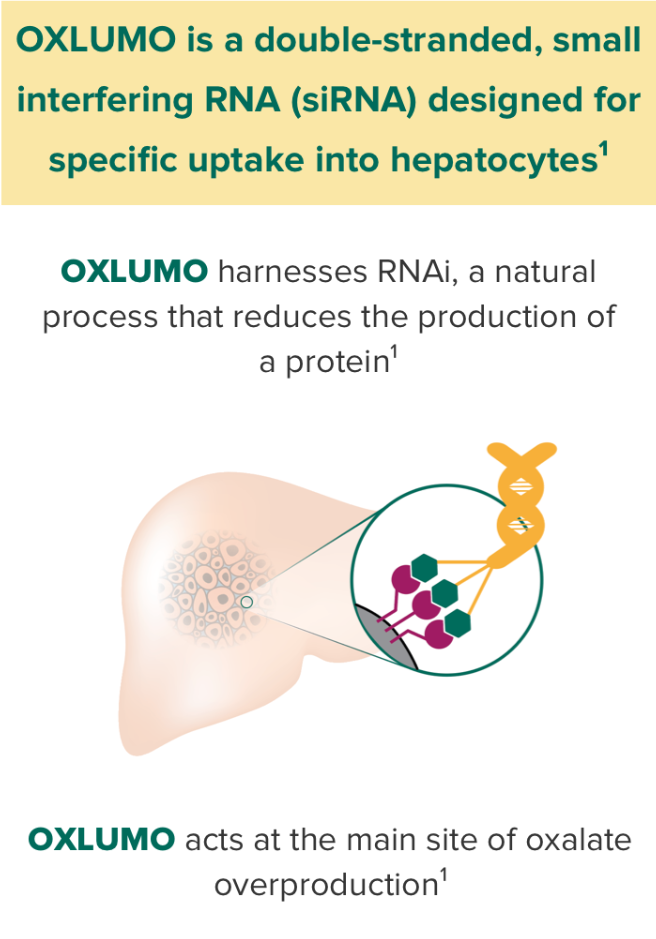
OXLUMO is an siRNA targeted specifically at the liver that harnesses RNAi, a natural process that reduces the production of protein.1
RNA, ribonucleic acid; RNAi, RNA interference; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
OXLUMO is an RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutic targeted to the liver1
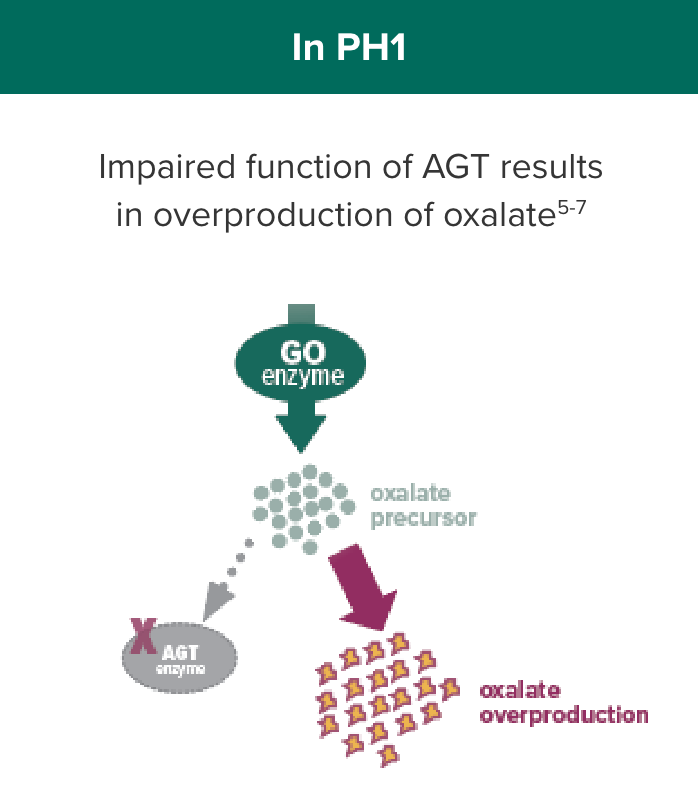
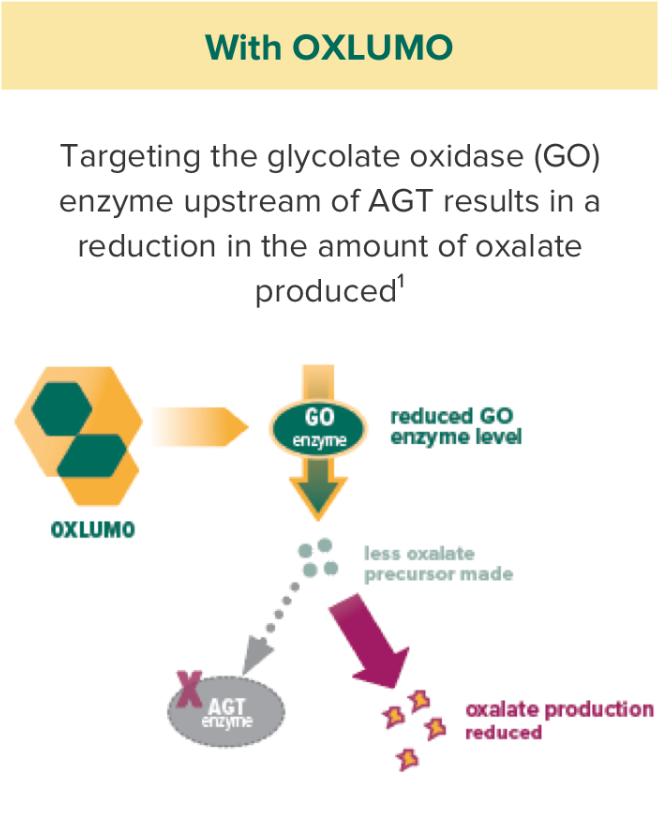
OXLUMO acts upstream of the metabolic defect in AGT to reduce oxalate production1
Providing relief with OXLUMO

“Before OXLUMO was available, our conversations with patients and families revolved around supportive care. Now that OXLUMO is available, we talk to patients about this medication that can actually treat the disease and not just manage its symptoms."
Mechanism of Action of OXLUMO
This video provides a brief overview of PH1 and how OXLUMO works.
Want to see how OXLUMO is dosed?
Use the dosing guide to learn which dosing regimen is right for your patient.
WANT TO SPEAK WITH AN OXLUMO REPRESENTATIVE?
Our representatives are available to provide detailed information about OXLUMO and how it may help your patients with PH1.
There’s more to learn about OXLUMO
When you sign up, we will keep you informed with updates and resources.
Alnylam Assist® provides support services for patients throughout their treatment with OXLUMO.
Alnylam Assist® includes patient services in 4 key areas, including understanding insurance benefits and financial assistance options for eligible patients,* helping ensure access to therapy, and providing PH1 disease education.
Patients must meet specified eligibility criteria to qualify for assistance. Alnylam reserves the right to make eligibility determinations and to modify or discontinue the program at any time.
1. OXLUMO [package insert]. Cambridge, MA: Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2. Liebow A, Li X, Racie T, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(2):494-503. 3. Hoppe B. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8(8):467-475. 4. Garrelfs SF, Frishberg Y, Hulton SA, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(13):1216-1226. 5. Milliner DS, Harris PC, Sas DJ, et al. GeneReviews®. University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2022. 6. Cochat P, Rumsby G. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(7):649-658. 7. Cochat P, Hulton SA, Acquaviva C, et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(5):1729-1736.
